
What is BMI? Understanding Normal Body Mass Index for Men and Women
What is BMI? Body Mass Index helps determine if you're underweight, normal weight, or overweight. Learn how BMI works for men and women.
High blood pressure is a well-known cardiovascular risk factor. It is sometimes difficult to prevent because of the absence of symptoms, and is often associated with excess weight. Often, if weight increases, so does blood pressure.
Your heart is an amazing organ, pumping five quarts of blood every minute and up to 2,000 gallons of blood per day. You may know that cardiovascular diseases are the number-one cause of death globally, killing an estimated 17.9 million people each year.
You may have heard that lifestyle changes can have a huge impact on your cardiovascular disease risk. But let’s take a closer look at heart health and weight, specifically, and see how losing extra pounds may help to lower blood pressure.
“The Nurses Health Study compared women with BMIs of less than 22 with those above 29 and found a 2- to 6-fold greater prevalence of hypertension among the obese."
Source: "Weight Loss and Blood Pressure Control" AHA Journals, 2008
As early as 1923, in "The blood pressure of healthy men and women", Dr. Brandreth Symonds established an association between weight and high blood pressure.
Today, weight and blood pressure are a major public health concern, given that they can have a major impact on the cardiovascular and renal systems of those who are overweight.
Learn more about the pathophysiological mechanisms that promote elevated blood pressure in people who are overweight.
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is when your blood pressure—or the force of blood pushing against the blood vessels—is too high. A blood pressure of 130/80 or higher is considered to be hypertensive, and a blood pressure of 120-29 and more than 80 is considered elevated, meaning you’re at risk for developing hypertension.
In 2018, the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association changed their blood pressure guidelines, eliminating the “prehypertension” category and lowering the definition of high blood pressure.
The CDC defines adult overweight and obesity as “weight that is higher than what is considered as a healthy weight for a given height.”
An adult who is 20 years of age or older is considered overweight if he or she has a body mass index (BMI) between 25 and 29.9, and obese if he or she has a BMI of 30 or more. While BMI may not tell the whole story when it comes to weight, it is widely used as a metric to determine overweight and obesity.
When talking about excess weight, we often refer to excess body fat. While not all obese individuals develop high blood pressure, scientific evidence supports that several pathophysiological mechanisms contribute to obesity-induced hypertension.
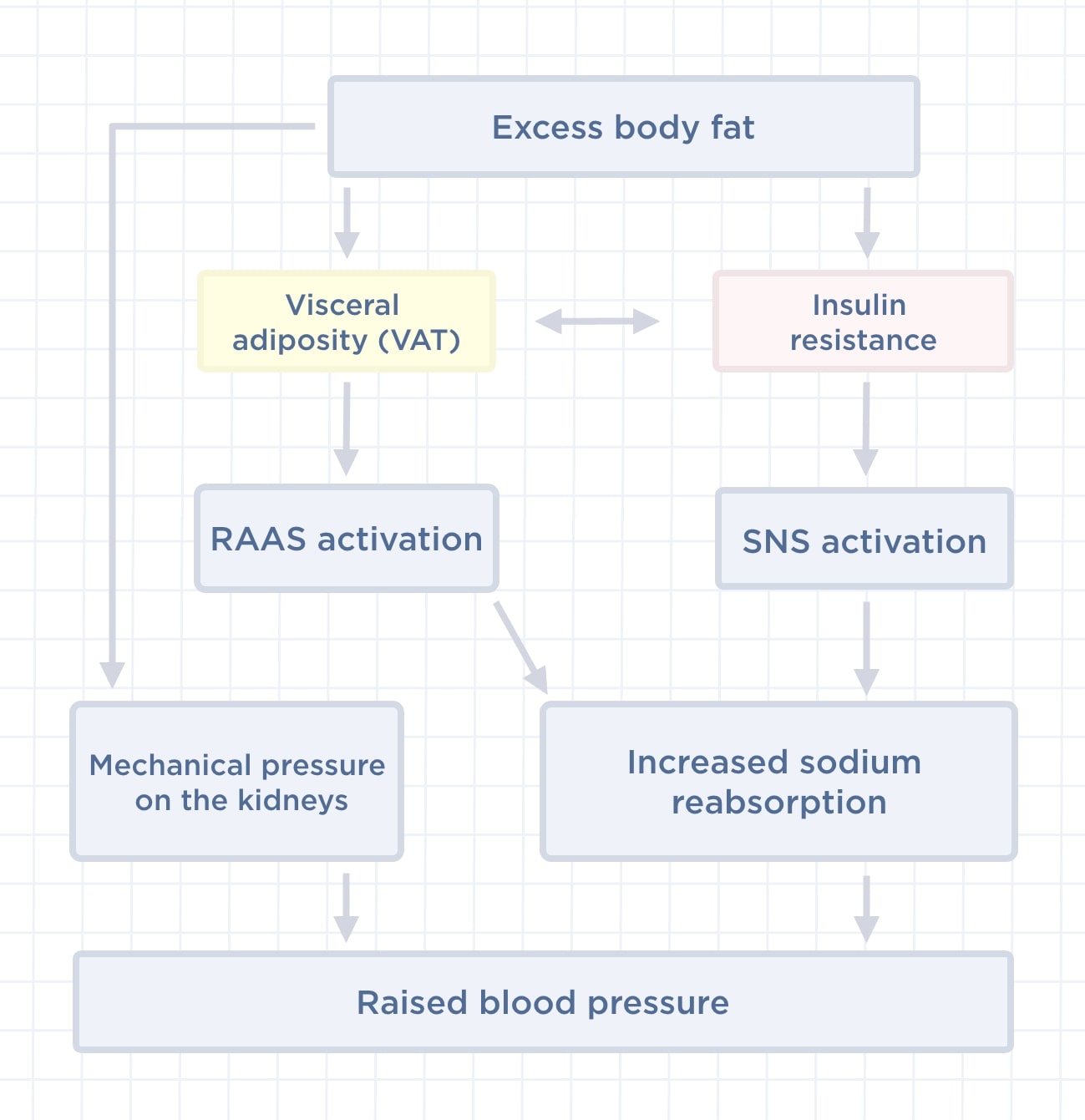
The sympathetic nervous system (or SNS) is a network of nerves that allows our brain to control blood pressure by adjusting the diameter of peripheral arteries through electrical impulses. In obese people, fat cells and insulin resistance tends to stimulate this sympathetic response.
Activation of the sympathetic nervous system has been considered to have an important function in the pathogenesis of obesity-related hypertension.
Source: "Mechanisms of obesity-induced hypertension" Hypertension Research, 2010
Too much visceral fat—the fat that is stored around the abdomen—can lead to abnormal compression of the kidneys or even a kidney injury that may progress. "Abnormal kidney function, which is associated with increased tubular sodium reabsorption, has a key role in initiating obesity-associated hypertension."
Source: "Obesity, kidney dysfunction and hypertension: mechanistic links" Nature Reviews Nephrology, 2019
These fat cell tissues secrete many hormones. In the kidneys, they can disrupt the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (or RAAS) responsible for sodium (salt) balance. The kidney must therefore maintain a higher blood pressure to excrete the daily intake of salt.
The association of VAT accumulation with high blood pressure can be confounded by several factors, including age, gender, degree of obesity, and glucose tolerance status; each of these factors has been shown to be related to both abdominal obesity and hypertension.
Source: "Visceral fat in hypertension: influence on insulin resistance and beta-cell function" Hypertension, 2004
When you are overweight or obese, the extra fat also increases vascular resistance, as well as the work the heart has to do to pump blood. This extra activity puts extra strain on your heart and causes higher blood pressure.
Extra weight can exacerbate other risk factors, such as high cholesterol and insulin resistance, that affect heart health. Insulin resistance is a particularly insidious cycle—the more fat you have, the more insulin resistant you become, causing you to secrete more insulin, causing you to store more fat. So blood pressure and diabetes are also linked.
Medical research to investigate many other possible relationships between excess body fat and high blood pressure is ongoing.
The CDC, too, has said that obesity increases the risk for heart disease and stroke —leading causes of death in the U.S.— and is often called the “silent killer” because it can have no symptoms. The longer you’re obese, the worse the effects can be, and the more complications can develop.
Heart failure
This severe complication refers to the inability of the heart to pump enough blood to properly supply the body’s organs with oxygen. The narrower the blood vessels, the greater the workload and the greater risk of heart failure.
Atrial fibrillation
High blood pressure can lead to an enlargement of the heart's left atrium, which then contracts abnormally. The resulting pulse disturbance is called an arrhythmia. Also, activity of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), as seen in people with obesity-induced hypertension can also lead to AFib. Read about AFib +
Coronary artery disease
If high blood pressure is not treated, the accumulated pressure on the walls of the arteries can make them more vulnerable. This is called arteriosclerosis, when the arteries become narrowed and promote the accumulation of plaque. Coronary artery disease occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart are blocked.
Valvular heart disease
A 2019 study published in the European Heart Journal showed that as BMI and fat mass increase, so does the risk of aortic stenosis, a condition in which the valve controlling the blood flow to the aorta fails to fully open.
Treatment resistance
A joint statement from the European Association for the Study of Obesity and the European Society of Hypertension indicates that obese patients are prone to arterial hypertension, require more medication, and have an increased risk of becoming treatment-resistant.
Ischemic stroke
High blood pressure is one of the leading cause of strokes, especially if it's associated with obesity. Indeed, excess fatty tissues cause reactions and inflammations that enhance the attachment of particles causing generation of clots in the (already weakened) brain arteries. If the brain is no longer irrigated, enough with oxygen-rich blood, the brain cells will begin to die.
Kidney failure
According to the American Heart Association, ”the nephrons in the kidneys are supplied with a dense network of blood vessels, and high volumes of blood flow through them. Over time, uncontrolled high blood pressure can cause arteries around the kidneys to narrow, weaken or harden.” Obesity is also a known risk factor for chronic kidney diseases (CKD).
Experts are clear: weight reduction can be crucial to lowering hypertension.
In an article form Circulation, researchers stated, “Although it is not precisely known to what extent weight reduction alone may be effective in controlling or preventing the lesser degrees of hypertension, the control of obesity should be an intrinsic part of any therapeutic or preventive antihypertensive regimen.”
Another publication in the Journal of Family Practice, the authors noted that a weight loss of 4kg via a change in diet reduced systolic blood pressure by 4.5 mm Hg and diastolic blood pressure by 3.2 mm Hg. In addition, they noted that weight loss of 1 to 1.2 kg may cause small reductions in systolic or diastolic blood pressure.
If you’re concerned about weight, check with your doctor to come up with a weight goal that’s right for you.
Many experts suggest setting SMART goals—specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound goals—to achieve long-term weight loss. You might also think in terms of process goals—e.g., walking 10,000 steps a day, vs. losing a certain number of pounds. In addition, consider body composition—your percentages of fat, water, and bone mass.

In a study Withings conducted with Georges Pompidou Hospital in Paris, researchers found that a decrease in BMI of 1.0 kg/m2 over a month was associated with a drop in blood pressure of 1.79 mmHg for men and 1.81 mmHg for women.
Another study published in Obesity Research in 2012 recommends a gradual and modest weight loss, defined as 5% to 10% of your baseline weight.
According to researchers, this level of weight loss “can normalize blood pressure levels even without reaching ideal weight,” and has been shown to be able to lower or even discontinue antihypertensive medication.
The researchers state that the lower blood pressure probably results from an increase in insulin sensitivity and a decrease in the activity of the sympathetic nervous system.
Blood Pressure UK also says that “you do not have to reach your ideal BMI to see results.”
Changes in diet and exercise can make a big difference if you’re trying to control blood pressure. The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute has issued guidelines that include lifestyle adjustments to help prevent and treat hypertension. Among them: losing weight (for every 20 pounds you lose, you can drop systolic pressure 5-20 points), and eating a lower-fat diet that’s high in fruits and vegetables.
And in an article published in the Journal of Family Practice, researchers conducted a meta-analysis of 8 randomized controlled trials with a total of 2000 patients. They found that weight loss achieved through diet changes reduced blood pressure in hypertensive patients.
First, it’s important to know that weight gain is essential during pregnancy, and if you’re concerned about weight, it’s best to check with your doctor.
High blood pressure during pregnancy can be dangerous. It may lead to decreased flow of blood to the placenta, placental abruption (in which the placenta separates from the inner wall of your uterus before delivery), premature delivery, and cardiovascular disease, among other risks.
There are various types of high blood pressure that can occur during pregnancy, including gestational hypertension, chronic hypertension, and preeclampsia, a dangerous condition that’s associated with 10-15% of maternal deaths.
Excess weight during pregnancy may play a role in the development of high blood pressure. A 2019 study published in Revista de Saúde Pública found that in pregnant women with excessive weight gain had higher mean systolic blood pressure at the beginning of the third trimester, compared to women with adequate or insufficient weight gain.
If you’re overweight or obese and have high blood pressure during pregnancy, what can you do? A 2019 study in Hypertension and Metabolic Syndrome suggests entering pregnancy at a lower BMI, avoiding weight gain, and taking low-dose aspirin.
The researchers suggest that home monitoring of blood pressure may also be helpful.
If you’re concerned about blood pressure and obesity, know that there are ways to control blood pressure and even reduce blood pressure with lifestyle changes. Consider lowering your blood pressure by aiming for realistic weight goals and increasing your activity levels to establish a healthy weight. Even a moderate amount of increased walking may help. Don’t give up, and keep moving!

What is BMI? Understanding Normal Body Mass Index for Men and Women
What is BMI? Body Mass Index helps determine if you're underweight, normal weight, or overweight. Learn how BMI works for men and women.

Healthy body composition: What it is and how to improve it
What is body composition? Learn how to measure it, what defines a healthy body composition, and tips to improve your fat, muscle, and water...
AFib: Atrial fibrillation symptoms and diagnosis
What is AFib? Learn about atrial fibrillation, its signs, symptoms, and risks like stroke or heart failure, plus how to detect and manage...
on your first order by registering
By registering, you agree to receive advertising e-mails from Withings. However, if you change your mind, you can unsubscribe at any time. *The discount is valid for any purchase (except BeamO and U-Scan Nutrio) of at least €100 for 30 days after reception of the code. Only valid on withings.com, and while supplies last. This offer is only valid for first-time purchases. These offers cannot be combined.