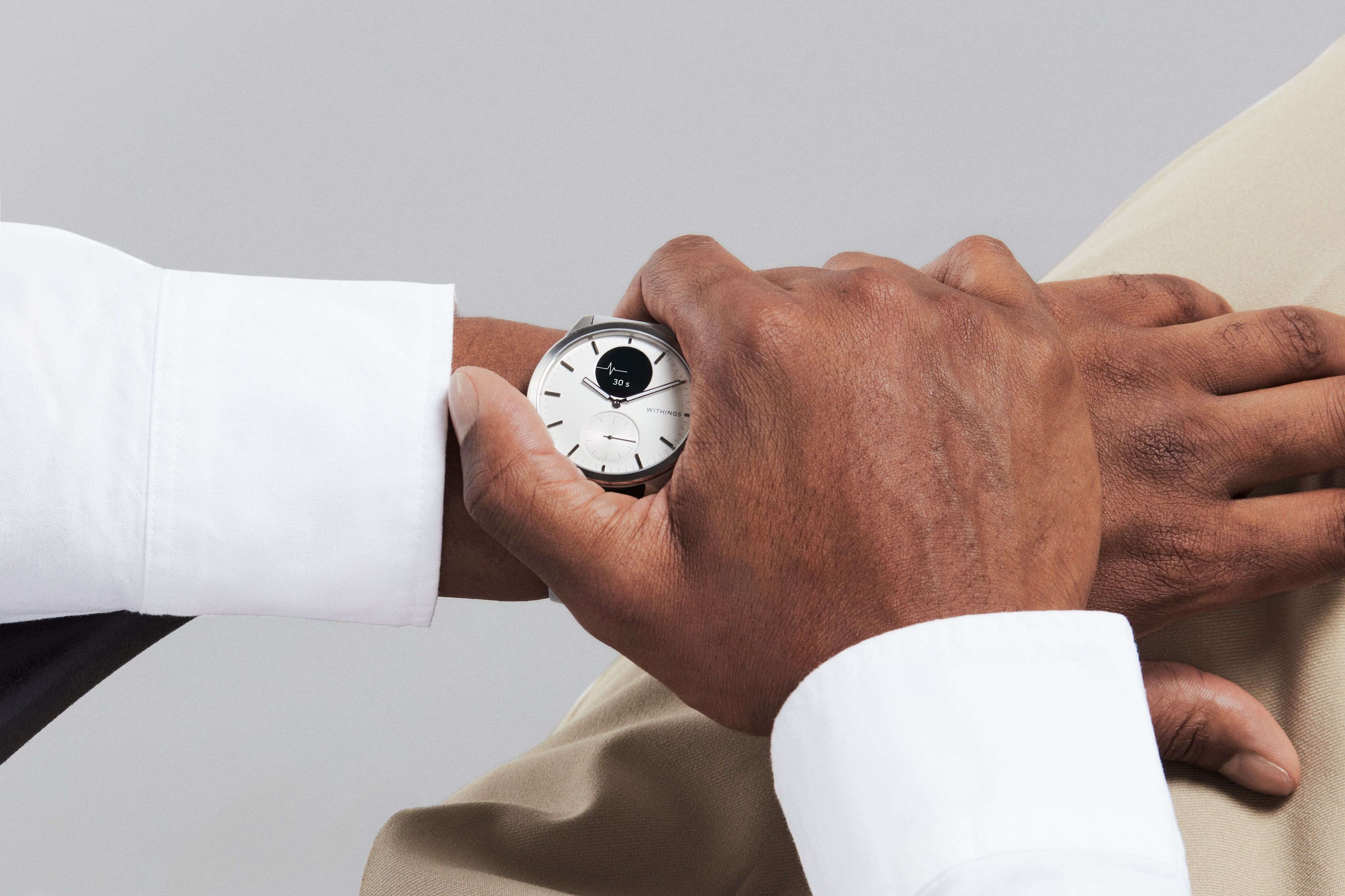

ECG watches: Perform an electrocardiogram anytime, anywhere
Monitor your heart health daily with our ECG watches, designed to track and analyze your heart's activity for optimal wellness and peace of...
Abbreviated ECG or EKG, an electrocardiogram provides vital information about the electrical activity of your heart. It is a key element in the detection of various cardiac complications.

An ECG is the graphical representation of the heart’s electrical activity recorded via electrodes. It can detect many cardiovascular pathologies.
With each heartbeat, an electrical signal travels through your heart. This signal causes your heart to contract and pump blood.
The role of an electrocardiogram is to record and amplify this electrical activity for a few seconds. It takes the form of a wave on a graph that reproduces cardiac cycles. Doctors can deduce the heart rate and rhythm by interpreting the tracing.
Heart rate gives you information about how fast your heart beats. The speed can vary as a result of physical activity, emotional responses and certain pathologies.
According to the European Society of Cardiology, "a normal heart rate usually averages 60 to 80 beats per minute (b.p.m.)."
Source: Escardio.org
A normal heart rhythm originates from the sinus node within the atrium. This electrical stimulus causes the heart ventricles to contract and pump out blood. Some dysfunctions may cause other heart tissues to start an impulse that will disturb the normal electrical sequence. The heart beating out of its normal rhythm is called an “arrhythmia.”
An electrocardiogram is traditionally recorded at rest, by placing small sensors called electrodes on the patient’s skin.
They are connected to an ECG recording machine, which traditionally has been used in a hospital or medical office. ECG recordings have moved out of the hospital environment with the emergence of wearable and mobile measurement systems. Whether in a medical setting or at home, the principle of recording an ECG remains the same, even if the method for obtaining the record differs.
Usually, this non-invasive test lasts from a few seconds to a few minutes. It is painless and has no side effects.

A normal heartbeat on the ECG graph will show the time the electrical wave takes to move through your heart.
By measuring time intervals on an ECG, health practitioners can see whether this electricity travel is too slow, normal, too fast, or even irregular. There are 3 distinct patterns:
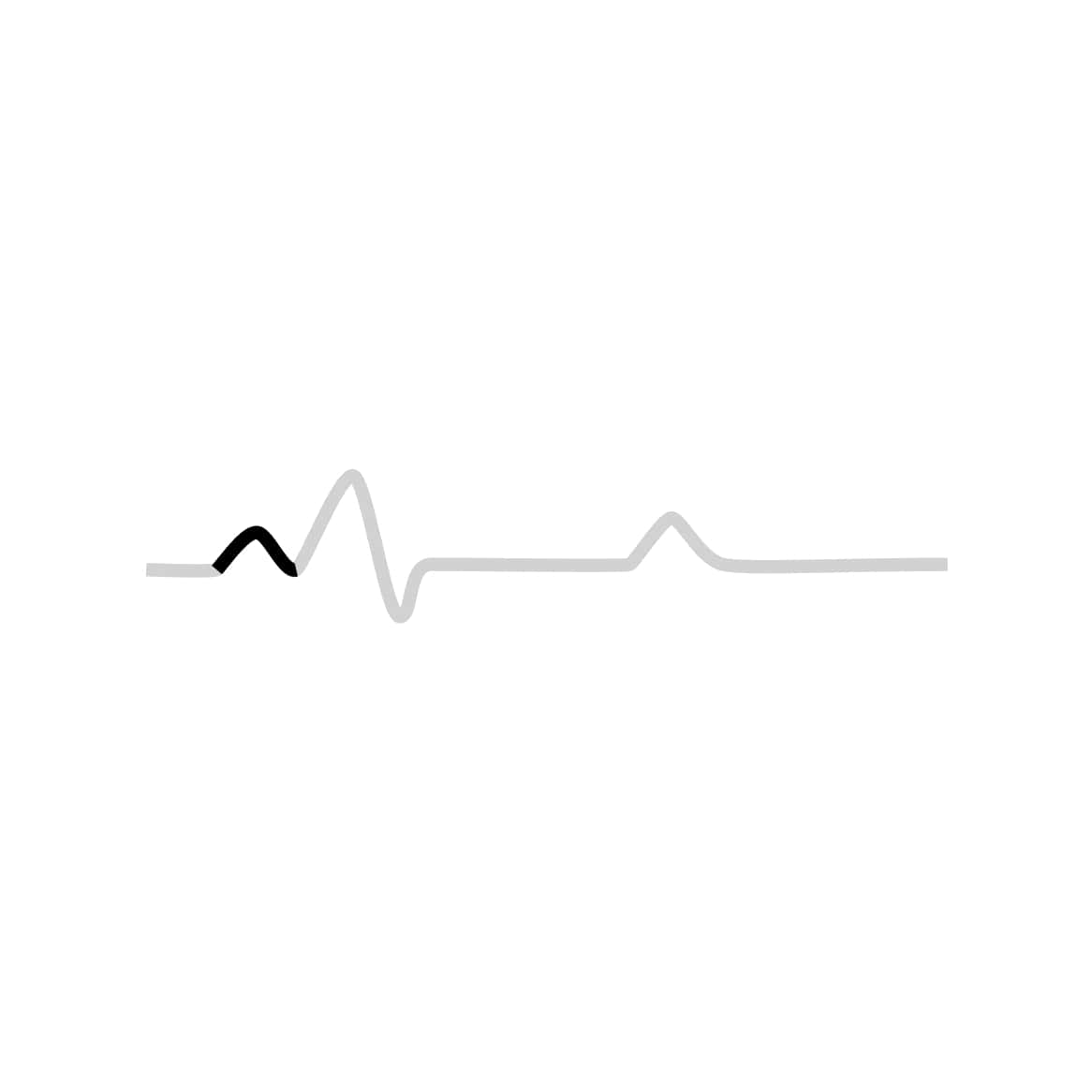
The graph shows a first electrical wave as electricity moves into the left and right atrium.
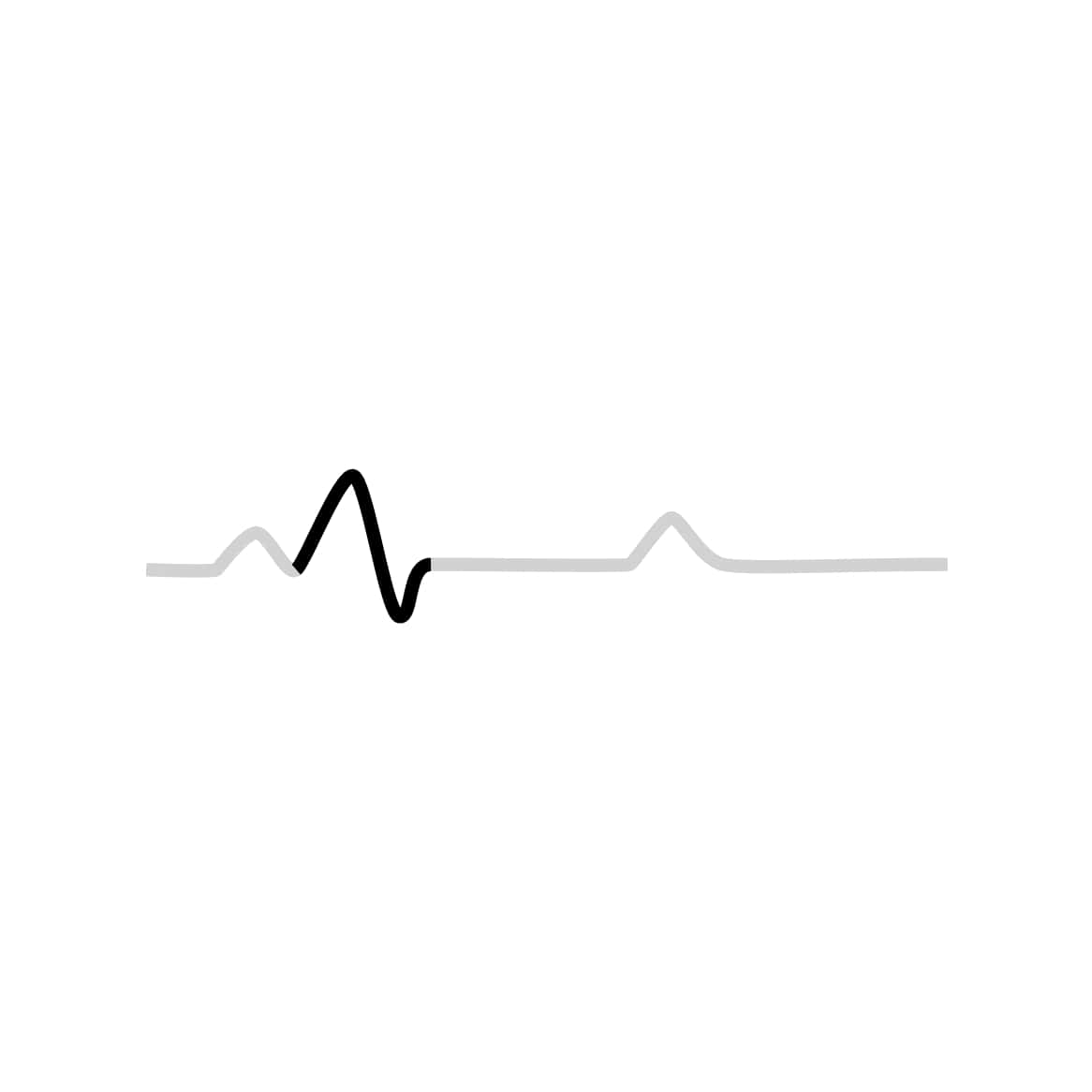
This second pattern shows electricity moving through the right and left ventricles.
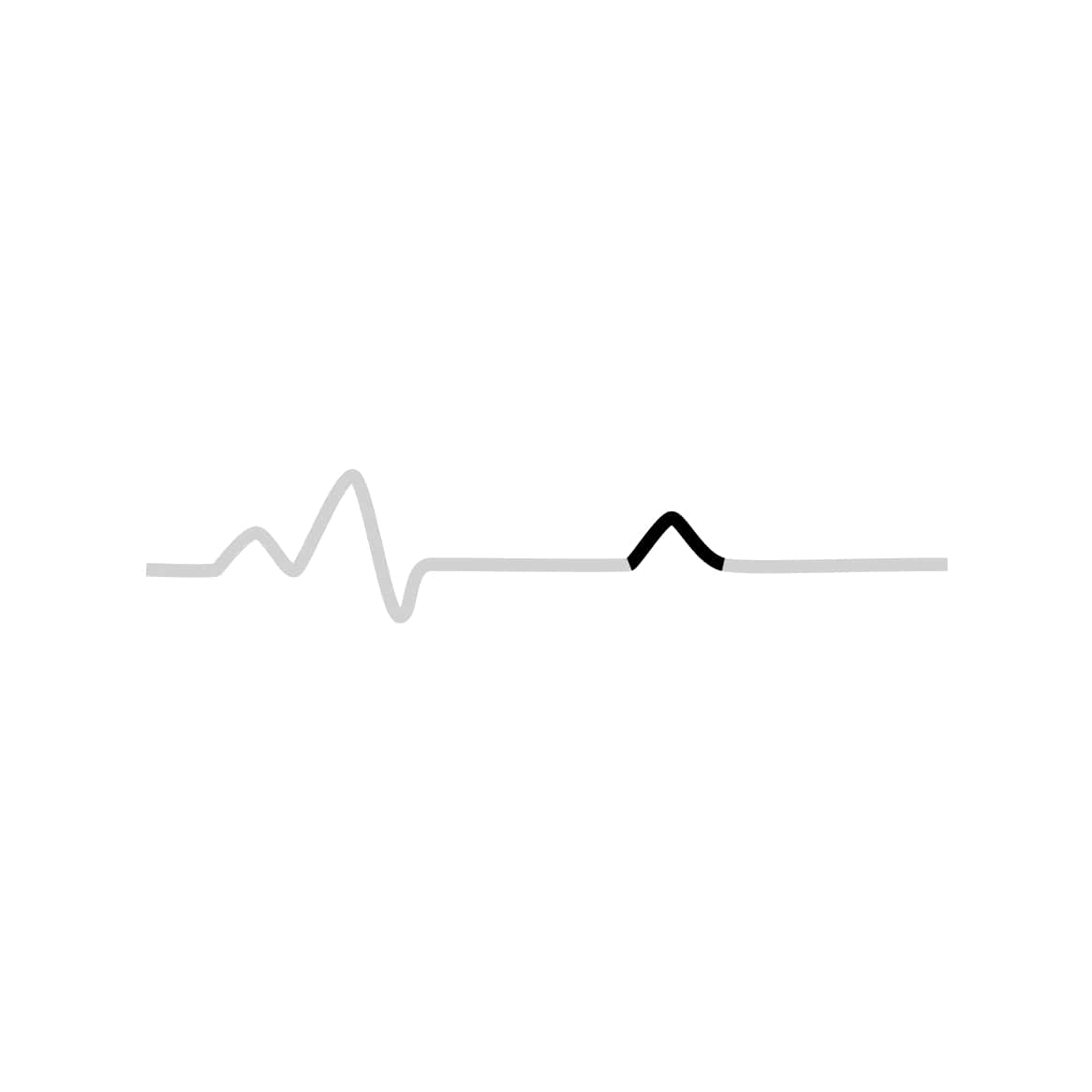
The final wave represents the return to a resting state for the ventricles.
ECG measurements are particularly important for people who present the symptoms of certain arrhythmias such as:
• Chest pain
• Shortness of breath
• Irregular or heavy heartbeats
• Loss of consciousness
Furthermore, an ECG is also of interest for people having the following risk factors :
• A family history of heart disease
• High blood pressure
• Advanced age
• Obesity
• Diabetes
• Cholesterol
Arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation (or AFib). This is an anomaly of the heart’s electrical activity.
Electrocardiograms* performed by Body Scan only detect AFib and do not cover the detection of other heart issues, including:
• Myocardial infarction. It happens when an artery that supplies blood to the heart becomes obstructed. Deprived of blood and oxygen, the heart muscle is damaged.
• Various other heart dysfunctions can be diagnosed by a cardiologist based on ECG results.
ECGs records a normal sinus rhythm for the following heart issues and followup tests are required to make a diagnosis.
Often caused by other heart conditions that damage the heart, it occurs when the heart’s pumping function is not strong enough to drive oxygen-rich blood to the body.
Also called VHD, they affect how the heart valves function to regulate blood flow into and out of the heart.
Some life-threatening heart diseases such as atrial fibrillation may be challenging to diagnose because AFib episodes may not occur at the doctor’s office. Keep your cardiac risk in check with our on-demand electrocardiogram solutions.

ECG watches: Perform an electrocardiogram anytime, anywhere
Monitor your heart health daily with our ECG watches, designed to track and analyze your heart's activity for optimal wellness and peace of...

Women smartwatches: Elegant and health-focused wearables
Discover Withings' elegant women's smartwatches. Track heart rate and sleep with advanced health features. Shop now!
Pulse Wave Velocity: Measurement, Devices, and How to Reduce It
Pulse Wave Velocity is a key metric for assessing cardiovascular health. Learn how it’s measured, devices that track it, and ways to...

Weight and heart disease: How weight loss reduces cardiovascular risk
Discover how excess weight increases heart disease risk and how weight loss can improve cardiovascular health, reduce heart failure, and...
on your first order by registering
By registering, you agree to receive advertising e-mails from Withings. However, if you change your mind, you can unsubscribe at any time. *The discount is valid for any purchase (except BPM Vision) of at least €100 for 30 days after reception of the code. Only valid on withings.com, and while supplies last. This offer is only valid for first-time purchases. These offers cannot be combined.